causes of post op fever
 WeeklyMedReview No. 4 - Causes of Postoperative Fever | Science Medicine Life
WeeklyMedReview No. 4 - Causes of Postoperative Fever | Science Medicine LifePostoperative fever Postoperative fever refers to a high body temperature (≥38.5°C) that occurs after a recent surgical procedure. Diagnosis of the cause of postoperative fever may sometimes be difficult; while fever in this context may be benign, self-limited or unrelated to the surgical procedure, it may also be indicative of a surgical complication, such as infection. Postoperative feverContentsCauses[ ]The most common causes of postoperative fever are often summed up for medical students at first with the letter W. The classic list consists of five W: Wind, Water, Sound, Walking and Wonder Drugs, but also two other causes should be considered: Wing/Waterway and (W)abscess. There is a characteristic time frame after surgery when many of these complications tend to develop (postoperative days or POD). Category Day Description Wind POD 1-2 lungs, that is, aspiration and pulmonary embolism; it has been commonly cited as cause of postoperative fever, but lacks evidence of support Water POD 3-5 , possibly associated with catheter (if a urinary catheter was inserted during surgery or remains in place at present i.e. ) Wound POD 5-7 surgical incision infection, whether superficial or deep (W)abscess POD 5-7 organ or space infection Walking (or VEINS pronounced as "Weins") POD 5+ (risk may persist for months after operation) or I wonder drugs or "What did we do?" Always or reaction to blood products, either to Wing/Waterway Always blood flow infection, phlebitis or cellulite related to intravenous lines, either central or peripheral Other major causes of early postoperative fever that are omitted from this list include, a life-threatening but treatable response to anesthetic and paralytic inhalers. Early postoperative fever (i.e., within the first 48 hours after the operation) has often been attributed to atelectasis, or spine, but it is highly likely to be part of a natural and non-infectious inflammatory response (with the involvement of the sympathetic nervous system) to the sustained tissue injury during the surgery; usually it does not require any medical intervention except antipyrethics and extra intake of fluid. Workup[]The diagnosis of postoperative fever is guided by possible etiologies in differential diagnosis. The patient's surgical and postoperative course should be checked in detail, noting whether the patient has been using a incentive spirometer or not regularly, if a Foley catheter was in place, what medicines he received, etc. The patient should be asked if he has any pain (and where?) or other symptoms such as cough or dysuria, which can help locate the source of the fever. A thorough physical examination, auscultation of the lungs, erythema or drainage of the surgical incision, evaluation of sites IV, noting edema of the lower extremity, etc. Laboratory tests and images are usually deducted for the evaluation of the fever that occurs in the first 48 hours after the operation, unless indicated by specific findings in history and physical examination. Beyond 48 hours, the test routinely includes urine and blood cultures, as well as chest X-ray. Popular culture[ ]In the medical drama Grey Anatomy, Meredith Grey refers to this mnemonic: "Wind, water, wound, walking, wonders. 5 Ws. Most of the time is wind; styling or pneumonia. Pneumonia is easy to assume. Especially if you're too busy to test. " ###################### #################################################################################################################################################################################################################################### cold Aches and and Several .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal}heat cold Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Languages
Tyler Larsen on Twitter: "1/ Does atelectasis cause post-operative fever? I occasionally hear atelectasis listed in the differential diagnosis for early post-op fever (EPF) but this idea has never made much physiologic

Post op fever- pod#3- uti
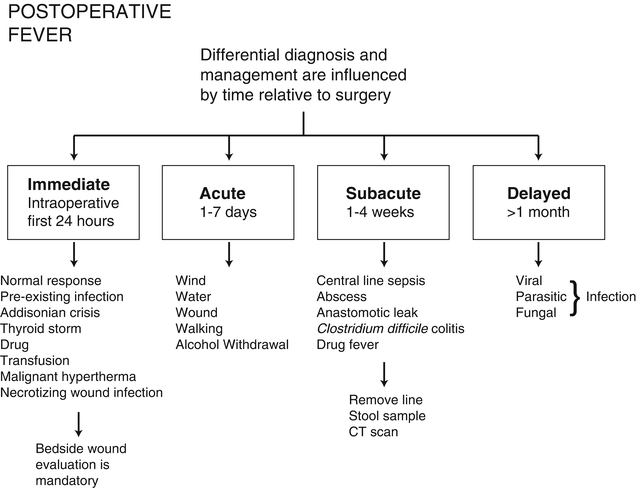
Postoperative Fever | SpringerLink

42 – Postoperative Fever | PAINE Podcast and Medical Blog

Postoperative Nonpathologic Fever After Spinal Surgery: Incidence and Risk Factor Analysis - ScienceDirect

Causes of postoperative fever | Medical school studying, Fundamentals of nursing, Surgery nursing

219 Post-Op Care and Complications with Avital O'Glasser MD - The Curbsiders
Causes of post op fever Mnemonics

PDF) Fever After Maxillofacial Surgery: A Critical Review
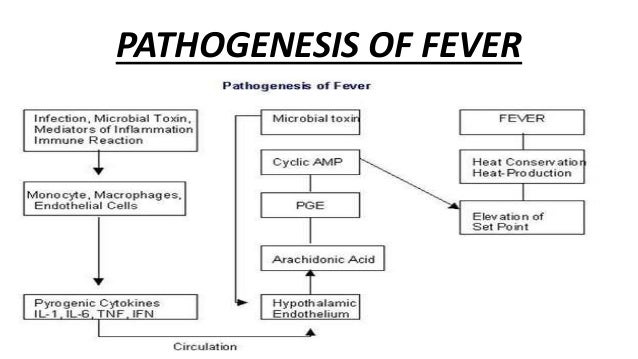
Post operative fever
/temperature-after-surgery-3156832-02-5b5626b646e0fb00371d6a4f.png)
When Does Fever After Surgery Become a Concern?
PLOS ONE: Postoperative Fever: The Potential Relationship with Prognosis in Node Negative Breast Cancer Patients
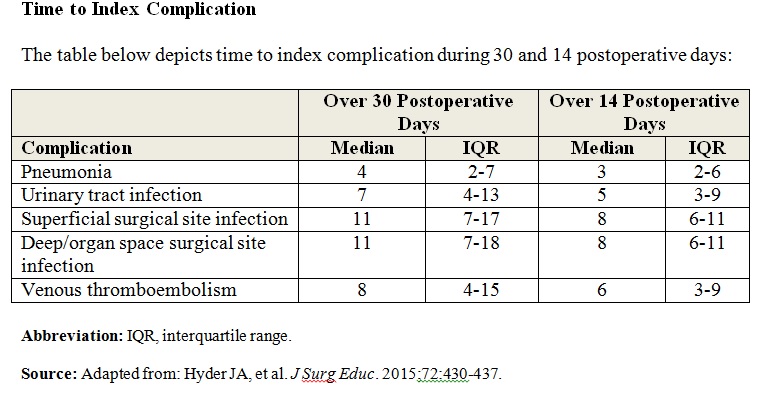
Postoperative Complications: Revising the Rule of W | Physician's Weekly

Surgery – Post-operative complications. | Archer USMLE Step 3 Blog

Common causes of fever in pediatric postoperative cardiac patients | Download Scientific Diagram
Fever in the Postoperative Patient

Postoperative fever
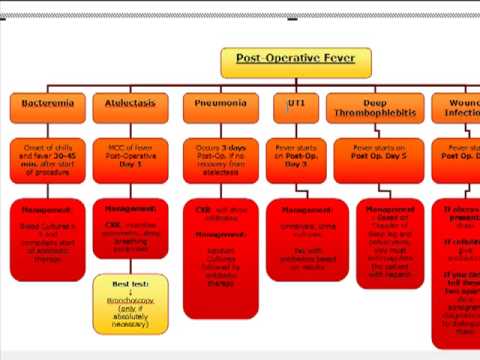
Surgery Algorithm: Post-Operative fever - YouTube
emDOCs.net – Emergency Medicine EducationPost-Surgical Complications - emDOCs.net - Emergency Medicine Education

Postoperative Fever. - ppt video online download

PPT - Post Operative Fever PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:6772803

42 – Postoperative Fever | PAINE Podcast and Medical Blog

Table 1 from Fever in the postoperative patient. | Semantic Scholar
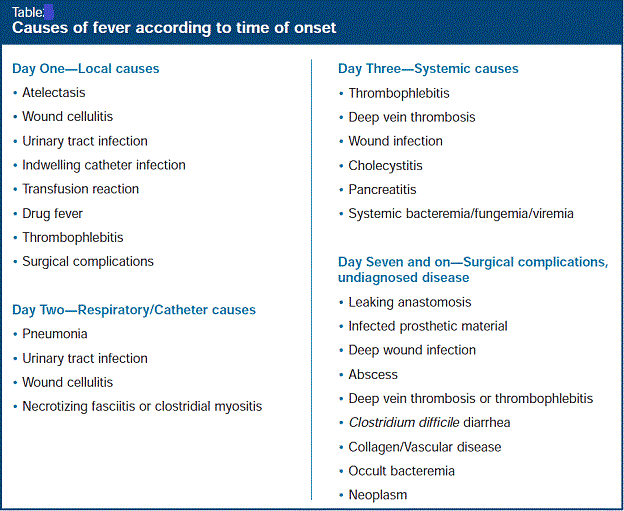
postoperative fever-1 – Dr Rajiv Desai
Fever Evaluation, Complication and Treatment in Surgical Patients :: Science Publishing Group
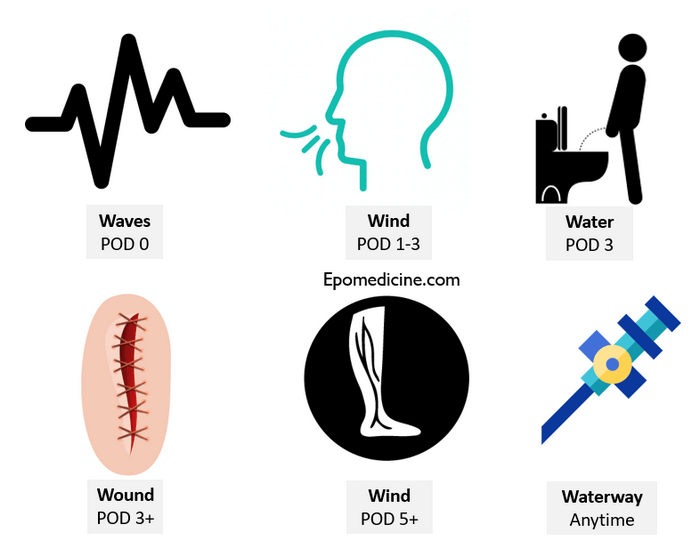
Postoperative fever - Rule of W (Mnemonic) | Epomedicine

USMLE Shortcuts- Post Operative Fever causes (5W's?) - YouTube

Approach to postoperative fever in pediatric cardiac patients Gupta AK, Singh VK, Varma A - Ann Pediatr Card

Post-op fever causes: the 5 w's. Also lung infection, FVD, sepsis, perioperative heart attack | Med surg nursing, Nursing school tips, Lung infection

Postoperative Complications Flashcards | Quizlet

postoperative fever - SurgeryPaper
Neuroscience Files on Twitter: "The "five Ws" mnemonic of most common causes of postoperative fever in the order in which they occur. 🤮🤢🥵 From the "Atlas of Infections in Neurosurgery and Spinal
Post-Operative Fever-Causes Mnemonics

Post Operative Fever - Surgeon's Envy

The potential role of postbronchoscopic fever on the postoperative outcomes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer - Zhu - Journal of Thoracic Disease

Atelectasis as a Cause of Postoperative Fever - CHEST

Management of postoperative fever in oral and maxillofacial surgery patients - ScienceDirect

PPT - Postoperative Fever PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:661293
![PDF] Causes and Management of Postoperative Fever | Semantic Scholar PDF] Causes and Management of Postoperative Fever | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/9c048f5935ecc1491184ba08190fe923ab96f055/3-Table1-1.png)
PDF] Causes and Management of Postoperative Fever | Semantic Scholar
Bioline International Official Site (site up-dated regularly)
Posting Komentar untuk "causes of post op fever"